A recently discovered document proves that Boeing ignored requirements FAA and international regulators made when they certified Boeing’s 737 MAX airliner.
The underlying problem:
For commercial reasons Boeing wanted the new 737 MAX version to handle like the old ones. But changes in the new version required an additional system to handle certain flight situations. The development of that system and the safety analysis of its implications were rushed through. Pilots were not informed of it and not trained to counter its failure.
Certification Demanded Training That Boeing Failed To Deliver.
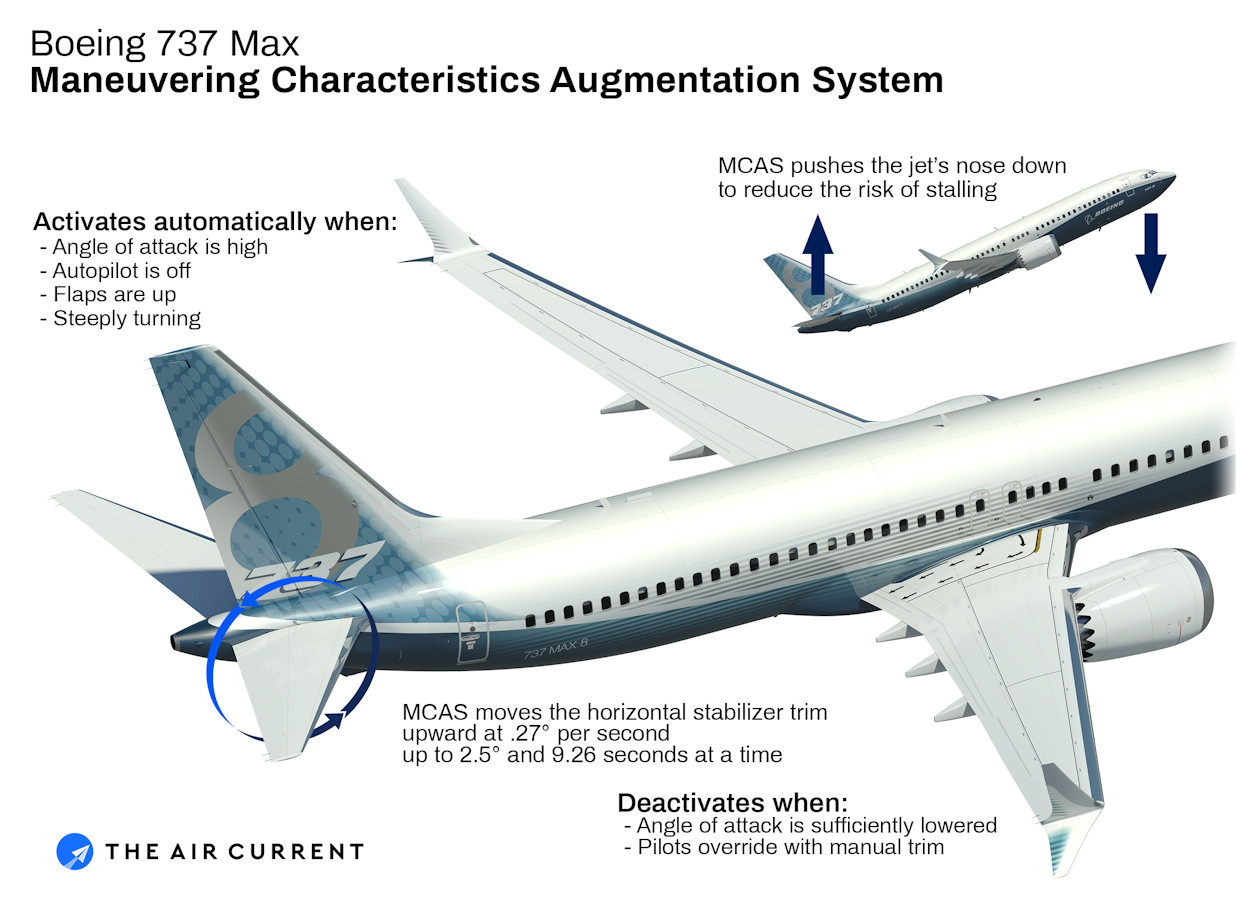
The added ‘maneuver characteristics augmentation system’ (MCAS) depended on only one sensor. When the sensor provided false data MCAS engaged and pointed the planes towards the ground. Manual trim using the plane’s trim wheel was required to regain flight stability. The pilots were not aware of that. The regulators who certified the plane as safe were unaware of the extend of the problem:
The MCAS system is poorly engineered and the design should never have been certified in the first place because it is in no compliance with Fail-Safe concept. But the issue is even worse. The certification that was given relied on false data.
The first MCAS design, on which the safety analysis and certification was based, allowed for a maximum trim movement by MCAS of 0.6 degree of a maximum of 5 degree. Flight tests proved that to be too little to achieve the desired effects and the maximum movement was changed to 2.5 degree.
No safety analysis for the much greater movement was conducted. The FAA and foreign regulators were not informed of it. Their certification of the 737 MAX was based on misleading data.
But even those certifications were only conditional. They required from Boeing to include relevant training material that explained the MCAS trim system and its potential problems to the pilots.
The original certification for the 737 MAX was issued by the U.S. regulator FAA. The European regulator EASA based its certification on the one the FAA provided but it added several of its own requirements. There is now documentary evidence that Boeing neglected to fulfill at least one of those requirements.
The one page document, first described by Reuters, is included in the Explanatory Note Issue 10(pdf) to the EASA Boeing 737 type certification which was issued in February 2016.
Page 15 of the Explanatory Note discusses “Longitudinal trim at Vmo”. Vmo is the maximum operational speed. The trim sets the nose of the plane up or down, independent of other pilot input. Too high up and the plane with lose lift and stall, too low down and the plane will hit terrain.
A failure of the MCAS system could trim the nose down. As a countermeasure the pilots would have to switch the trim system off. They would then manually trim the plane back into a level flight. This was a concern. The EASA note says:
Subsequent to flight testing, the FAA-TAD expressed concern with compliance to the reference regulation based on an interpretation of the intent behind “trim”. The main issue being that longitudinal trim cannot be achieved throughout the flight envelope using thumb switch trim only.
EASA considered the need to use manual trim “unusual”. But it allowed it to pass because the required training material would “clearly explain” the issue:
The need to use the trim wheel is considered unusual, as it is only required for manual flight in those corners of the envelope.
The increased safety provided by the Boeing design limits on the thumb switches (for out-of-trim dive characteristics) provides a compensating factor for the inability to use the thumb switches throughout the entire flight envelope. Furthermore, the additional crew procedures and training material will clearly explain to pilots the situations where use of the trim wheel may be needed due to lack of trim authority with the wheel mounted switches.
Without the additional procedures and training material the 737 MAX would not have been certified. By providing the plane without the required training material Boeing essentially handed incomplete planes to its customers.
The FAA is as regulator far too cozy with lobbyists and aircraft manufacturers. It outsources too much of the certification testing to the manufacturers. It should not have allowed Boeing to install a MCAS that depended on a sole sensor.
But the bigger culprit here is clearly Boeing. The plane was developed in a rush. Even its own engineers doubted that it was safe:
Rick Ludtke, a former Boeing engineer who worked on designing the interfaces on the MAX’s flight deck, said managers mandated that any differences from the previous 737 had to be small enough that they wouldn’t trigger the need for pilots to undergo new simulator training.That left the team working on an old architecture and layers of different design philosophies that had piled on over the years, all to serve an international pilot community that was increasingly expecting automation.
“It’s become such a kludge, that we started to speculate and wonder whether it was safe to do the MAX,” Ludtke said.
MCAS was not the only change that made the 737 MAX a ‘kludge’. The design errors were inexcusable. Boeing did not inform the regulators when it quadrupled the maximum effect the MCAS system could have. These changes had side effects that were not properly analyzed. Failure of the system was hazardous and extremely difficult to handle. Indicators lights showing that the system may have failed, a safety feature, were sold as extras.
Briefly: This whole adventure will dearly costly for Boeing
Source: Moon of Alabama


